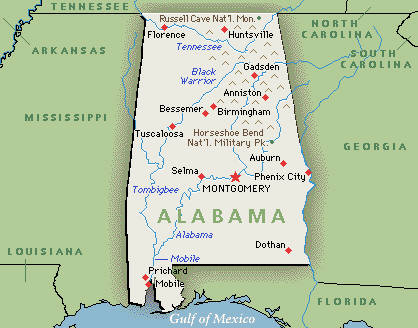
Alabama, “The Heart of Dixie,” is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States, bordering the Gulf of Mexico to the south. From the American Civil War until World War II, Alabama suffered economic hardship, in part because of continued dependence on agriculture. Following World War II, Alabama experienced growth as the economy of the state transitioned to one with diversified interests. The establishment AND expansion of multiple United States Armed Forces installations added to the state economy and helped bridge the gap between an agricultural and industrial economy.
Alabama is unofficially nicknamed the Yellowhammer State, after the state bird. Alabama is also known as the “Heart of Dixie”. The state tree is the Longleaf Pine, the flower is the Camellia. The capital of Alabama is Montgomery. The largest city by population is Birmingham. The largest city by total land area is Huntsville. The oldest city is Mobile, founded by French colonists. The total population of the state based on the latest census, is 4,822,023. The 2015 population of Alabama is not precisely known, nor is there a projection for 2016.
Geography and Climate
Alabama is the thirtieth-largest state in the United States with 52,419 square miles of total area. It is also the 23rd in the amount of surface water, with 3.2% of the surface area being water. Alabama contains the second-largest inland waterway system in the US. About three-fifths of the land area is a gentle plain with a general descent towards the Mississippi River and the Gulf of Mexico. Alabama ranges in elevation from sea level to over 1,800 feet in the Appalachian Mountains. The highest point is Mount Cheaha, at a height of 2,413 ft. Alabama’s land consists of 22 million acres of forest.
Alabama’s climate is humid subtropical with an average annual temperature of 64°F. Temperatures tend to be warmer in the southern part of the state, while the northern parts of the state tend to be slightly cooler. Summer in Alabama notoriously hot, with high temperatures averaging over 90 °F. Alabama is also prone to tropical storms and hurricanes. South Alabama reports many thunderstorms. The Gulf Coast averages between 70 and 80 days per year with thunder reported. This activity decreases somewhat further north in the state, but even the far north of the state reports thunder on about 60 days per year. Occasionally, thunderstorms are severe with frequent lightning and large hail. Alabama ranks seventh in the number of deaths from lightning and ninth in the number of deaths from lightning strikes per capita.
[wp_ad_camp_1]
The peak season for tornadoes varies from the northern to southern parts of the state. Alabama is one of the few places in the world that has a secondary tornado season in November and December, along with the spring severe weather season. The northern part of the state is one of the areas in the U.S. most vulnerable to violent tornadoes.
Winters are generally mild in Alabama, with average January low temperatures around 40 °F in Mobile and around 32 °F in Birmingham. Although snow is a rare event in much of Alabama, northern areas of the may receive a dusting of snow a few times every winter. Alabama’s highest temperature of 112 °F was recorded on September 5, 1925 in Centerville. The record low of −27 °F occurred on January 30, 1966 in New Market.
Basic History of Alabama
 Indigenous peoples of varying cultures lived in the area for thousands of years before European colonization, and among the historical tribes of Native American people living in the area of present-day Alabama at the time of European contact were Iroquoian-speaking Cherokee, and the Muskogean-speaking Alabama (Alibamu), Chickasaw, Choctaw, Creek, and Koasati. Most Native American tribes were completely removed from the state within a few years of the passage of the Indian Removal Act by Congress in 1830.
Indigenous peoples of varying cultures lived in the area for thousands of years before European colonization, and among the historical tribes of Native American people living in the area of present-day Alabama at the time of European contact were Iroquoian-speaking Cherokee, and the Muskogean-speaking Alabama (Alibamu), Chickasaw, Choctaw, Creek, and Koasati. Most Native American tribes were completely removed from the state within a few years of the passage of the Indian Removal Act by Congress in 1830.
The French founded the first European settlement in the region at Old Mobile, in 1702. The city was moved to the current site of Mobile in 1711. Most of what is now the northern two-thirds of Alabama was known as the Yazoo lands beginning during the British colonial period. It was claimed by the Province of Georgia from 1767 onwards. What is now the lower one-third Alabama was made part of the Mississippi Territory upon its creation in 1798. The Yazoo lands were added to the territory in 1804.
[wp_ad_camp_2]
The Alabama Territory was created by the United States Congress on March 3, 1817. On January 30, 1846, the Alabama legislature announced the new state capitol, Montgomery, after several other cities had served this purpose. By 1860 the population had increased to a total of 964,201 people, of which 435,080 were enslaved African Americans and 2,690 were free people of color. Alabama was under military rule from the end of the war in May 1865 when it slaves were freed under the 13th amendment until its official restoration to the Union in 1868. From 1867 to 1874, with most White citizens barred from voting, many African Americans emerged as political leaders in the state.
On January 11, 1861, Alabama declared its secession from the Union. After remaining an independent republic for a few days, it joined the Confederate States of America. The Confederacy’s capital was initially located at Montgomery. Alabama was heavily involved in the American Civil War. During Reconstruction, state legislators ratified a new state constitution in 1868 that created a public school system for the first time and expanded women’s rights. Legislators funded numerous public road and railroad projects. Organized resistance groups also tried to suppress the freedmen and Republicans. These included the Pale Faces, Knights of the White Camellia, Red Shirts, Ku Klux Klan, and the White League.
Reconstruction in Alabama ended in 1874, when the Democrats regained control of the legislature and governor’s office. They wrote another constitution in 1875, and the legislature passed the Blaine Amendment, prohibiting public money from being used to finance religious affiliated schools.
 In 1900, Alabama had more than 181,000 African Americans eligible to vote. By 1941, more White Alabamians than African American Alabamians had been disfranchised: 600,000 Whites to 520,000 African Americans.Nearly all African Americans had lost the ability to vote. The 1901 constitution reiterated that schools be racially segregated. It also restated that interracial marriage was illegal, although it had already been against the law since 1867. Further racial segregation laws were passed into the 1950s. The Rosenwald Fund began funding the building of what came to be known as Rosenwald Schools for African American education. A total of 387 schools, seven teacher’s houses, and several vocational buildings had been completed in the state by 1937. Several of the surviving school buildings in the state are now listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
In 1900, Alabama had more than 181,000 African Americans eligible to vote. By 1941, more White Alabamians than African American Alabamians had been disfranchised: 600,000 Whites to 520,000 African Americans.Nearly all African Americans had lost the ability to vote. The 1901 constitution reiterated that schools be racially segregated. It also restated that interracial marriage was illegal, although it had already been against the law since 1867. Further racial segregation laws were passed into the 1950s. The Rosenwald Fund began funding the building of what came to be known as Rosenwald Schools for African American education. A total of 387 schools, seven teacher’s houses, and several vocational buildings had been completed in the state by 1937. Several of the surviving school buildings in the state are now listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
Tens of thousands of African Americans left Alabama in the early 20th century as part of the Great Migration to industrial jobs and better futures in northern industrial cities. Reflecting this emigrations, the population growth rate in Alabama dropped by nearly half from 1910 to 1920. At the same time, many rural people moved to Birmingham to work in new industrial jobs. Birmingham experienced such rapid growth that it was called “The Magic City”. By the 1920s, Birmingham was the 19th largest city in the United States and had more than 30% of the Alabama’s population. Between 1940 and 1943, more than 89,000 people moved into the city to work for war effort industries. Cotton and other cash crops faded in importance as the state developed a manufacturing and service base.
Although efforts had already started decades earlier, African Americans began to more actively attempt to end the disfranchisement and segregation in the state during the 1950s and 1960s with the Civil Rights Movement. These efforts directly led to the enactment of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and Voting Rights Act of 1965 by the U.S. Congress. During the Civil Rights Movement, African Americans achieved a protection of voting and other civil rights through the passage of the national Civil Rights Act of 1964,and the Voting Rights Act of 1965. Legal segregation ended in the states as Jim Crow laws were invalidated or repealed.
attempt to end the disfranchisement and segregation in the state during the 1950s and 1960s with the Civil Rights Movement. These efforts directly led to the enactment of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and Voting Rights Act of 1965 by the U.S. Congress. During the Civil Rights Movement, African Americans achieved a protection of voting and other civil rights through the passage of the national Civil Rights Act of 1964,and the Voting Rights Act of 1965. Legal segregation ended in the states as Jim Crow laws were invalidated or repealed.
We will be publishing a projected 2015 and 2016 population figure for the state of Alabama as soon as that information becomes available as well as some religious demographics and a map.